Upper School.
Age 14-18 : Classes 9-12
The journey into young adulthood.
As pupils mature into older teenagers, their desire to argue, debate, challenge, think critically, explore and move towards adulthood becomes the driving force to learning.
Our Waldorf three dimensional approach to education continues in the Upper School integrating academics with immersive experience, arts, crafts, and sports, however in this third phase, the focus is on abstract, in depth, critical thinking with an emphasis on the ability for analysis.
To support intellectual development, our curriculum takes students beyond a superficial understanding of subjects and requires students to explore issues in depth with intensive focus.
The curriculum also builds on developing each student’s personal responsibility and independence, along with social and civic awareness and our small class sizes mean that pupils have expert academic attention and support.
Classes 10, 11, 12 students study the NZCSE, an international Waldorf qualification, recognised by UCAS and accepted by UK universities and on a par with A-Levels and International Baccalaureate. The qualification is points-based and involves continuous assessment that is both internally and externally moderated.
In Class 10 pupils spend an hour per week studying GCSE Maths & English Language respectively, enabling them to qualify to apply for a UK Government student loan.








Class 9: age 14-15
-

Literacy
The History of Drama and Theatre including tragedy and comedy. Enabling students to see different points of view, we examine a range of emotions from social and psychological perspectives.
The Narrative Tradition explored through:
- Novels and short stories
- Development of characters and literary devices
- Shakespeare: structure and language
-

Mathematics
Mathematical Rhythms, Patterns and Sequences
- We put mathematics into an historical context and trace the threads in a developing tapestry of connections and relationships and enter a world of deepening abstractions. Here mathematics becomes more than the conventional learning and application of principles, methods and techniques: it is through the identification and development of the rhythms of number patterns that students develop an intuitive grasp of processes, principles and concepts that lead to and support a deeper intellectual understanding.
• Geometry - Plane and Solid Geometry - Conic Curves are constructed, their properties investigated and the relationships between the different curves explored.
-

Physics & Engineering
Concepts are understood through students learning about the inventors and technology of the 19th and 20th Centuries and the relationship between the machines and the consciousness that accompanies their use.
Topics include heat and its relationship to the development of engines, from the early steam engines to modern internal combustion engines.
-

Foreign Languages
French
German - Creation of a German Audio Drama, including its performance and recording
-

Art History
The History of Art /Aesthetics
- The origins of the Western tradition are explored from Ancient Egypt through Greece to Rome and Early Christian art leading to the Middle Ages and the dawn of the Italian Renaissance.
-
Physiology and Anatomy
Study of the human skeletal and muscular system and the sense organs
-
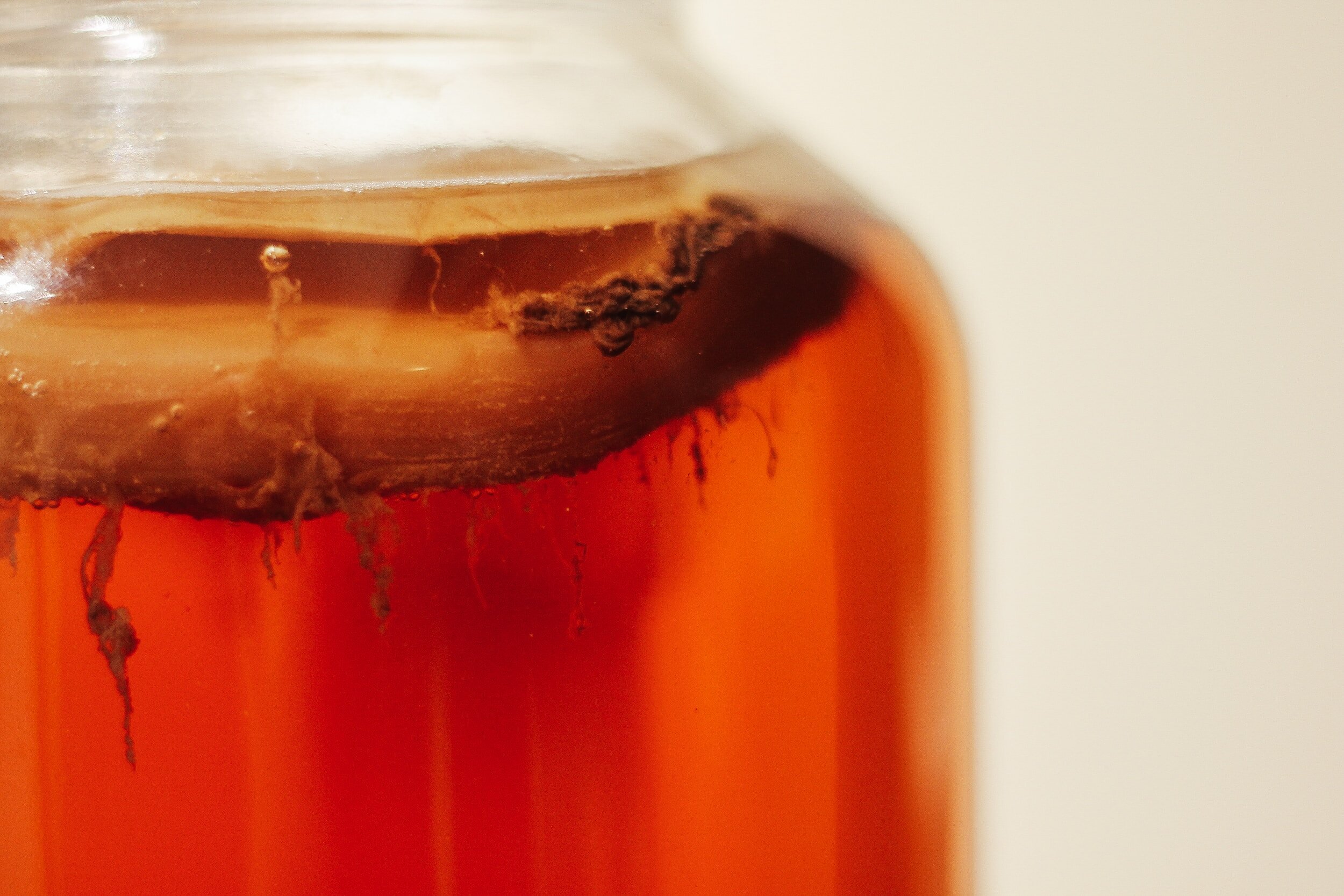

Organic Chemistry
Study includes:
the role of carbon and its compounds
the rarefaction and solidification of products starting from glucose
production of alcohols, fossil fuel extraction
natural and industrial organic compounds and their polymers; characteristics
production and use of starch, cellulose, wood, coal, wax and oil..
Experimental investigation includes fermentation and distillation; fossil fuels
-

Modern History
These lessons awaken an interest in the world and enable students to understand the historical forces that create the current global situation. Covering the start of a new millennium, the end of Cold War and its proxy conflicts with Asia and Africa, the end of Colonialism and the resulting complex world, themes around ideology and propaganda, and the globalisation of both the world economy and communications systems.
-

Human Geography
Human Geography such as analysing population, migration and relating it to the land itself, linking to History Main Lessons.
-

Politics
-

Arts
- Drawing
– ‘Chiaroscuro’ - light and shadow in painting and drawing. - Modelling – clay modelling and sculpture within the Platonic solids geometry lesson; plaster casting; casting with other materials; techniques for mask making; woodcarving; soft stone carvings. • Basket Making
-

Physical Geography
Tectonic and Geomorphological processes, including erosion and volcanic activity.
-

Handwork
Looking at Fibres, structure and recycled fashion
• Pattern creation and cutting; Dress-making
-

Sport & Movement
-

Craft
• Woodwork – carpentry and joinery to make shelves, lidded boxes, toolboxes, steps etc. teach accurate measurement and self-assessment of quality.
Copper beating
Blacksmithing
-

Ceramics
-

Practical Geometry
Understanding, calculating and creating the geometry of Conic Sections




Class 10: age 15-16
-

English Language
From Myth to Literature - The transition from pre-literate cultural forms such as myth, saga, and religious ritual to the origins of literature, with its shift from collective to individual experience.
Poetry – Pupils examine different poetic forms and look at how words can be used non-literally, delving deep into the rhythms and sounds of the natural world through language. Pupils learn how to understand and to compose different styles of poetry.
-

Mathematics
Algebra - Exploring principles, processes and methods and solving a wide range of algebraic and graphical problems.
• Trigonometry - Investigating the development and application of the fundamental principles of Trigonometry. Study includes the Theorem of Pythagoras and the Sine, Cosine, Tangent and Cotangent ratios for angles between 0° and 90° described and defined.
• Surveying - Practical application of Mathematics learned in Trigonometry. Students explain and demonstrate the use of surveying instruments to measure and record distances and horizontal angles and draw a scaled map with boundaries and topography.
-

Physics
Focus on Mechanics. Covering tensile and compressive forces, centre of area and centre of gravity, conditions for equilibrium, moments of forces, resolution of forces and the triangle and polygon of forces, elasticity, the stiffness of springs and Hooke’s Law.
Experiments in dynamics look at velocity and acceleration. Uniform acceleration as the result of gravity acting on a mass in free fall and the relationship between force, mass and acceleration will be investigated and discussed.
Potential and kinetic energy is explored and defined.
-

Physiology and Anatomy
Students study comparisons in the brain and nervous system with the study of the heart and circulations.
The brain’s relationship to perception, thought and memory provides a basis for discussing consciousness and moral aspects of conscience.
The relationship of the heart and circulation system to emotional experience is studied.
-

Inorganic Chemistry
Students study acids, bases, and salts and the reactivity series of metals through experiment, observation and analysis. They examine different minerals from the earth and consider how and from what they formed.
Students will look and make salt crystals, investigate the role of water in crystallisation, discover the qualities and reactivity of metals and start balancing reaction equations using words and symbols.
-

Social Sciences
The relationship of Early Civilisation to its geography; the dependence of people on the Earth, the climate, the resources, contrasting it with the present disconnection/independence from the natural world. Archaeological remains from the last Ice Age are studied to discover what they can tell us about the way people lived and interacted.
The development of the early civilisations of the Tigris and Euphrates, the Nile, the Indus river and Yellow river are studied: how they influenced each other, later civilisations and ultimately the culture of the modern world.
-

Foreign Languages
French & German
A study of international humorous texts, jokes and idiomatic expression to support the broadening of students’ social, psychological and cultural horizons.
-

Art
Drawing and Painting – Formal composition and principles of shaping a picture. Exploring colour, atmosphere and mood. The logic involved in planning pictures or designs that may need to be drawn in mirror form, or in which a composite picture is built up using several plats or blocks challenges the students’ power of thinking as well as the precision involved in the work.
• Print-making - applied to a range of media.
-

Philosophy
Pythagoras, Socrates, Confucius. Plato, and Aristotle and how the philosophers of the 5th and 6th Centuries BC influence modern thinking, including what it means to be human and the purpose of existence.
-

Geography
Study includes
Climate Change
Plate Tectonics
Geomorphology
Atmosphere
Ocean Circulation
Students also create and present a detailed study of a natural hazard.
-

English Literature
Shakespeare and Drama – Shakespeare’s texts and dramatic devices are analysed and dramatic characterisation and staging discussed and worked with practically.
-

Genetics & Sustainability
OUTDOOR LEARNING
Students develop their knowledge through gardening and farming, both in school and during external visits.
-

Craft & Handwork
• Dress making and tailoring – provide individual patterns relating to the rectangular shape of the woven cloth.
• Woodwork – provides the concepts of plumb, square and true
• Pottery – reinforcing science with an awareness of the perpendicular in relation to the horizontal plane.
• Metal work – understanding material, force, shape and process through practical work.
-

GCSE Maths
Sitting both GCSE Maths & English Language gives students the experience and skills of writing under examination condition and enables students to meet Government criteria for a Student Loan at University.
One hour per week for each is taken to prepare for the exams using subject knowledge gained from our Waldorf curriculum.
Our Class 10 GCSE results for 2023 were a 100% Pass with grades ranging from Grades 4-9.
-

GCSE English Language
Sitting both GCSE Maths & English Language gives students the experience and skills of writing under examination condition and enables students to meet Government criteria for a Student Loan at University.
One hour per week for each is taken to prepare for the exams using subject knowledge gained from our Waldorf curriculum.
Our Class 10 GCSE results for 2023 were a 100% Pass with grades ranging from Grades 4-9.
-

Sports
-

Personal Development
-

Drama
Class 11
As young adults, students of Class 11 start to develop a deep inner life as well as a maturing intellect. They have a greater level of objectivity and self-knowledge and begin to find an inner orientation between appearance and reality, between what is said and what is meant. They are challenged to find their own way, to make decisions and to consider the full consequences of their actions.
In support of this, the underlying themes for Class 11 are about morality and thinking and the development of an understanding that with knowledge there is power – which must be used wisely to be of service to others.

Class 11: Age 16-17
-

Literature & Language
An essential theme in literature and in the development of human thinking is the act of questioning.
Student’s examine:
Medieval Literature supported by study of other texts, such as Hamlet.
19th and 20th Century Literature: Blake, Shelley, Coleridge, Clare, Hawthorne and Keats.
The themes from Parzival are taken up in 19th and 20th Century literature. The questions of imagination, nature and nurture, the source of the artistic and the sublime and the threat which the Romantic period brought to expression.
Upper School Play - Performed by Classes 10 and 11, supported by Class 9.
-

Mathematics
• Geometry - The laws of Euclidean geometry are integrated into Projective Geometry. By considering the ‘infinitely distant elements’ (point at infinity, line at infinity, plane at infinity) the pupils learn to think about infinity.
• Trigonometry - Spherical Trigonometry extends and enhances Planar Trigonometry and studying vibrations creates a base for understanding Wave Theory and the background to wireless data transmission studied in the Class 11 Physics block.
-

Biology
Biology - The study of cells, microscopy and ecology, from microscopically small elements to the macroscopically large biosphere.
• Embryology – Reproductive systems and hormones, the human embryo, organ formation, the phases of birth, childhood and the human life journey. At the cellular level, cell structure, function and life processes are compared and discussed and human embryo development is compared with that of mammals.
-

Physics
Electromagnetic fields, radiation and radioactivity and the theories of the nature of matter are studied.
Physics and Chemistry are a coherent unit.
-

Chemistry
This year provides a general overview by looking at the individual character of the elements in the way the chemical substances interact. It includes the Periodic Table; the nature of science and the history of chemistry - connecting with Medieval History in alchemy and with Atomic Theory through the study of significant scientists and practical work; illustrating the concepts which led to the Periodic Table and how these elements and their compounds can be used in the world.
-

Foreign Languages
French & German: Study of the beauty of the language through the works of great poets of various periods.
-

History
How the western territories of the Roman Empire became ‘the first Europe’ and the roots of some of the institutions of modern Western Europe between the end of the 5th Century and the fall of Constantinople in 1453.
As well as the development and increasing political dominance of the Catholic church in the west, the relationship between church and state and the emergence of the Nation State, students look at the influence of Roman, Greek, Germanic, Judaic, Persian and Arabic cultures on education and scholarship, both in the west and in the Abbasid Empire, and the impact of Islam.
-

History of Art & Music
History of Art & Music of the 19th Century - studying composers such as Beethoven, Brahms, Dvorak along with artists including Goya and Turner,
Trips to the National Gallery, the Festival Hall and the Barbican.
History of Art
- Study of the arts of literature, painting, sculpture and music, to trace the development of Western culture from the Renaissance to the middle of the 19th Century. This creates a connecting thread between different areas of study across the curriculum in Class 11 and prepares the ground for the study of the culture of the 20th Century in Class 12.
-

Botany
Plants structures, functions, diversity and genetics. Students investigate photosynthesis, growth, reproduction, seed development and dispersal, and defence, along with the human relationship with plants for food and medicines.
-

Philosophy & Economics
- How the philosophy of the Ancient World was interpreted by the philosophers of the Middle Ages and the Enlightenment in the light of Christianity, Islam and the new scientific world-view, Out of this comes the development of the science of Economics, in the 18th Century.
- We examine the work of St. Paul, Bacon, Descartes, Goethe, Locke, the Physiocrats and Adam Smith, with additional contributions from figures such as St Augustine, Ibn Sina (Avicenna), Thomas Aquinas, Shakespeare, Rousseau, Voltaire, Kant, Spinoza and Hume.
-

Arts & Crafts
• Sculpture and Modelling – Focus on the human body and expressions of emotion.
• Drawing and Painting.
• Mask making in different cultures.
• Metal casting
• Stone and Woodcarving.
• Weaving – combining handwork and technology.
• Cardboard work and bookbinding
-

History of Art
Similarities and dissimilarities in the arts are examined between painting and sculpture with music and poetry.
Opposite concepts such as Impressionist and Expressionist become motifs for consideration of the role of art in expressing the struggle of human consciousness.
-

Sports & Physical Activity

Class 12: Age 17-18
-

Literature & Language
Both contemporary English Literature and World Literature, examining how literature reflects changing individual and cultural consciousness..
Students explore how to interrogate purpose, and developing and shaping complex arguments, eloquently articulating a stance
• Film Studies and Creative Writing
-

Mathematics
MATHEMATICS
• Projective Geometry - Building on the work in Class 11, Projective Geometry in Class 12 penetrates more deeply into the relationship between plane, line and point. The effect of infinitely distant elements is explored by constructing a sequence of measures of the line, forms using perspective and projective correspondences, asymmetrical rotations and plane path curves (spirals). Polar transformations are also constructed.
• Calculus - Building on Class 11 the differentials and integrals of the trigonometric, exponential and logarithmic functions are derived and defined. Parametric functions and implicit equation are differentiated. The area between various types of functions and the volumes of revolution generated by them is explored.
• Complex Number Theory
-

Physics
20th and 21st Century Physics - including Atomic Physics, Wave Systems, Electricity or Mechanics.
Optics - Students investigate new paths in the realm of optics. The applicability of quantum theory to the microcosm and of the theory of relativity to the macrocosm are combined in relation to the human experience.
Beginning with the sense of sight and by bringing thought to bear on the known facts concerning light, an attempt is made to find a relationship to the real nature of light.
-
Biochemistry
Students study the biochemistry of the body, specifically the gut system, and compare it with the biochemical substances and processes of other living organisms, such as the bee.
From this they expand the topic to consider the impact of chemicals on the environment and living organisms.
-

Biology
Evolutionary Biology - We look at different theories about evolution including Lamarck, Darwin, Steiner and modern scientific theory. Students investigate the evolutionary pathways of ‘human and animal’.
The resources of London’s museums and university research centres are used to explore and observe the teeth, skulls, skeletons and relics of our hominid ancestors and to compare them with animals such as the shark and the primates.
Students consider the impact of human development on local and global eco-systems, and look at anticipating the future and imagining the role of science in building sustainable futures.
-

Applied Statistics
Statistics applied to projects in various subjects including:
Biology
Chemistry
Geography
Ecology.
-

Foreign Languages
Foreign Languages (French & German)
-

Modern and Contemporary Art
“That art makes visible otherwise hidden cultural and psychological forces has long been recognised and has made it a tool for the cultural historian as well as the psychiatrist. It can be used to diagnose an age, a culture or a patient.”
We move from the 20th Century and up to the present: to discuss their work in the context of personal biographies as well as contemporary social and political issues; to ask what motivates them; to evaluate how well their work conveys their ideas; and to evaluate the ideas themselves.
After an overview of some of the main players in the major art movements of the first half of the 20th Century, students direct and lead the block through their own research and presentations according to their individual interests
-

Social Science - History
• Modern and Contemporary History – What characterised the Greco-Roman age? How did the Middle Ages differ from modern times? How are historical periods defined? Can one find the same stages of cultural evolution in geographical regions, such as the Far East in comparison to Europe?
History teaching in Class 12, complemented by sociology, undergoes a change of viewpoint. Earlier in the school the structure has been chronological.
Now different perspectives, processes and themes are studies that span large periods of time. This change of position enables the pupils to gain some understanding of the philosophy and methods of history as a science.
-

Social Science - Sociology
-

Social Science - Geography
Studies of changing communities over time in relation to natural, cultural, political and economic systems, plus an independent research project on a chosen community.
We use mathematical thinking and interpretation of data to better understand risks to people and the world, and to imagine mitigations and solutions to these issues.
We look at geography through the prism of democracy to understand the relationships between geographical location and culture and to understand the impact of geography on power and politics
-

Music in the 20th Century
Throughout history, music has served different needs in the society. In the Middle Ages, music was a tool for people to have communion with God, followed by Renaissance, Baroque, Classical and Romantic musical movements. Then came the violent 20th century where two World Wars were witnessed and rapid technological advancements like recording and broadcasting were made.
This is the context in which various divergent musical movements developed that is striving to make a break with the Austro-German musical tradition. Driven by new impulses and the trauma of the world wars, composers in the 20th century were searching for new answers, new paths to forge ahead together with the powerful tools that technology have provided. In this block, we would look at the various social, political, psychological impulses that were influencing the composers as well as their unique biographies that often determine which impulses were picked up to shape the musical movement they bring to the world.
After an overview of some of the main musical movements of the 20th Century, students direct and lead the block through their own research and presentations according to their individual interests.
-

Politics
Democratic Participation
Understanding the power of language and text in shaping and influencing political views.
Understanding how language and text can be used to manipulate people’s political thinking.
Linking to Mathematics we examine the power of data and statistics in shaping and influencing political views and understand how data and statistics can be used to manipulate people’s political thinking.
Linking to Biology we examine the motivations for technological and scientific development, and reflecting on the political aspects scientific progress.
-

Drama
Drama including::
Monologues
Physical theatre
Theatre design
Playwriting
Directing
Comedy and the history of drama
Class 12 Play - A full-scale drama production for all Class 12 students.
-

Cultural Studies
Culture of the 20th Century
-

Digital Technologies
-

Personal Project
-

Visual Arts
Understanding the interdependence of history, materials, science, technology, art, craft and performance in the development of societies and cultures.
Investigating the properties, limitations and potential of materials and tools.
Understanding the history of techniques, technologies and processes, and their impact on making and creating.
Asking questions of and answering questions through creative and aesthetic media.


